About the scheduling system
Scheduler is an advanced scheduling and eligibility management system that helps centres organise test sessions, allocate resources, and manage test centre room availability.
This article explains what the scheduling system is and what the benefits of integrating with it are.
In this section
Integrating with the scheduling system
Scheduler is designed to automate and optimise complex timetabling needs using a combination of constraint-based logic and powerful optimisation algorithms.
The Scheduler API ensures accurate and efficient data exchange between Scheduler, the Surpass Platform, and other platforms, such as scheduling portals. This combination allows you to leverage Scheduler’s scheduling system capabilities for Surpass tests via your own scheduling portal or similar external service.
The Scheduler methods/endpoints not currently in use include being able to create, update, and delete test centres, rooms and modules.
Scheduler Entities
Before integrating with Scheduler, it is beneficial to have an understanding of how its entities all relate to each other. The core Scheduler entities are:
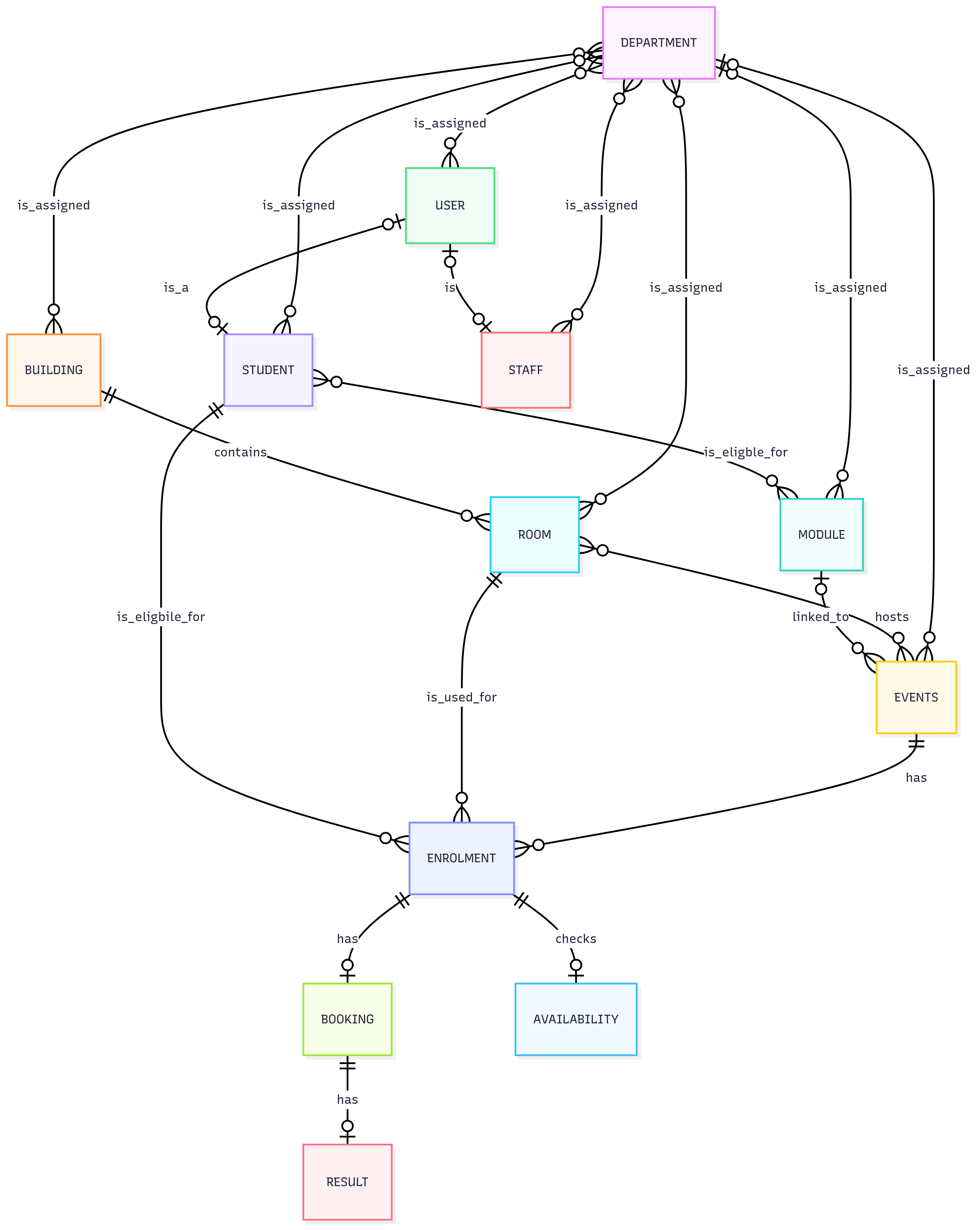
Terminology
Scheduler has its own standard terminology. The following table details how these terms correlate with Surpass terminology:
| Surpass | Scheduler |
|---|---|
| ID | OptimeIndex |
| Reference | ID |
| Name |
Description |
| Client |
Department |
| Region |
Site |
| Test Centre | Building |
| Test | Event |
| Candidate | Student |
| Test Booking | Enrolment |
Also note:
- Candidates have their own reference in Scheduler, as ‘Students’. However, if candidates require a log in to the Scheduler scheduling portal, you can create a ‘User’ account with the user type ‘Student’ and associate it with the ‘Student’ reference.
- Users in Scheduler can be either candidate user accounts or staff members, defined by the userType property.
- Modules are a container for tests (events) and candidates, and are a Scheduler-specific concept.
Further reading
Now you know what the scheduling system is, read the following articles to learn more:
